What is AI Ethics?
The field of AI ethics is about the rules and values guiding how artificial intelligence (AI) is made and used. It’s a set of ideas to make sure AI helps people, is fair, and respects everyone’s rights.
In the modern tech landscape, the importance of AI ethics has become paramount, with AI technologies forming a big part of life.
AI ethics helps avoid problems like AI biases or invasions of privacy – thus, it’s about making sure AI is safe and does good things without harming jobs or being misused.
As AI continues to evolve, having these ethical guidelines is key to making sure AI works well for everyone.
The Roots of AI Ethics
The roots of AI ethics can be traced back to the early days of AI development.
In the mid-20th century, as AI emerged as a field, pioneers like Alan Turing began contemplating its broader impacts, including ethical considerations. Turing’s famous paper, “Computing Machinery and Intelligence” (1950), sparked discussions about machine intelligence that would eventually lead to ethical considerations.
In the 1970s and 1980s, the rapid advancement in computing power brought AI into more practical use, raising concerns about privacy and decision-making biases.
Joseph Weizenbaum’s book, “Computer Power and Human Reason” (1976), reflects on the moral responsibilities of AI developers.
In the late 1990s and early 2000s, there was a significant shift in the world of AI, with a growing focus on ethical concerns. This era marked the beginning of a more serious conversation about the need for ethical guidelines in AI, although formal, widely accepted rules were not established yet.
This period was key in setting the stage for the development of more detailed AI ethics guidelines that came later.
These milestones laid the foundation for today’s AI ethics, which emphasizes transparency, accountability, and societal impact, balancing technological advancement with ethical responsibility.
Core Principles of AI Ethics
In a major study of 84 guidelines for AI ethics (Jobin et al., 2020), researchers identified 11 key principles that are essential for developing and using AI responsibly:
Principle
Description
Transparency
AI should be open about how it works and the decisions it makes, so everyone can understand and check it.
Justice and Fairness
AI should treat everyone equally and fairly, avoiding bias and making sure it doesn’t favor or harm certain groups.
Non-Maleficence
AI should not harm people or their well-being.
Responsibility
Those who make and use AI should be accountable for what it does, especially if something goes wrong.
Privacy
AI must protect people’s personal data and not misuse or share it without permission.
Beneficence
AI should actively do good things and improve people’s lives.
Freedom and Autonomy
AI should respect human choices and not control or limit them.
Trust
People should be able to rely on AI to be safe and work as expected.
Sustainability
AI should be made and used in ways that are good for the environment and society in the long run.
Dignity
AI should respect human values and not make people feel less important.
Solidarity
AI development should focus on helping society as a whole and supporting everyone.
AI Ethics in Application
In today’s fast-paced tech world, AI ethics is more than just a set of rules; it’s about making sure AI works fairly and safely for everyone.
This means taking the big ideas of AI ethics and making them work in real life. Here’s a closer look at how this happens.
Making Ethics Practical: It’s about turning broad ethical ideas into clear steps for building and using AI. For instance, to be fair, AI needs to be taught with diverse training data so it doesn’t favor one group over another.
Checking for Ethical Risks: Regularly testing AI to see if it could cause problems, like invading privacy or being biased.
Thinking About the User: Designing AI with the people who will use it in mind ensures it’s easy to use and respects their rights.
Following the Rules: AI has to stick to laws and guidelines, like those for protecting personal information.
Listening to Feedback: Letting users report issues with AI helps make it better and safer.
Teamwork Across Fields: Experts from different areas like ethics, law, and technology work together to tackle AI’s ethical challenges.
Diverse Development Teams: Including people from various backgrounds in AI development is crucial. It helps bring different perspectives, reducing the risk of biases and ensuring the AI is fair and inclusive.
Teaching Ethics: Making sure people who create and manage AI know about ethics and how to apply them.
Challenges and Controversies in AI Ethics
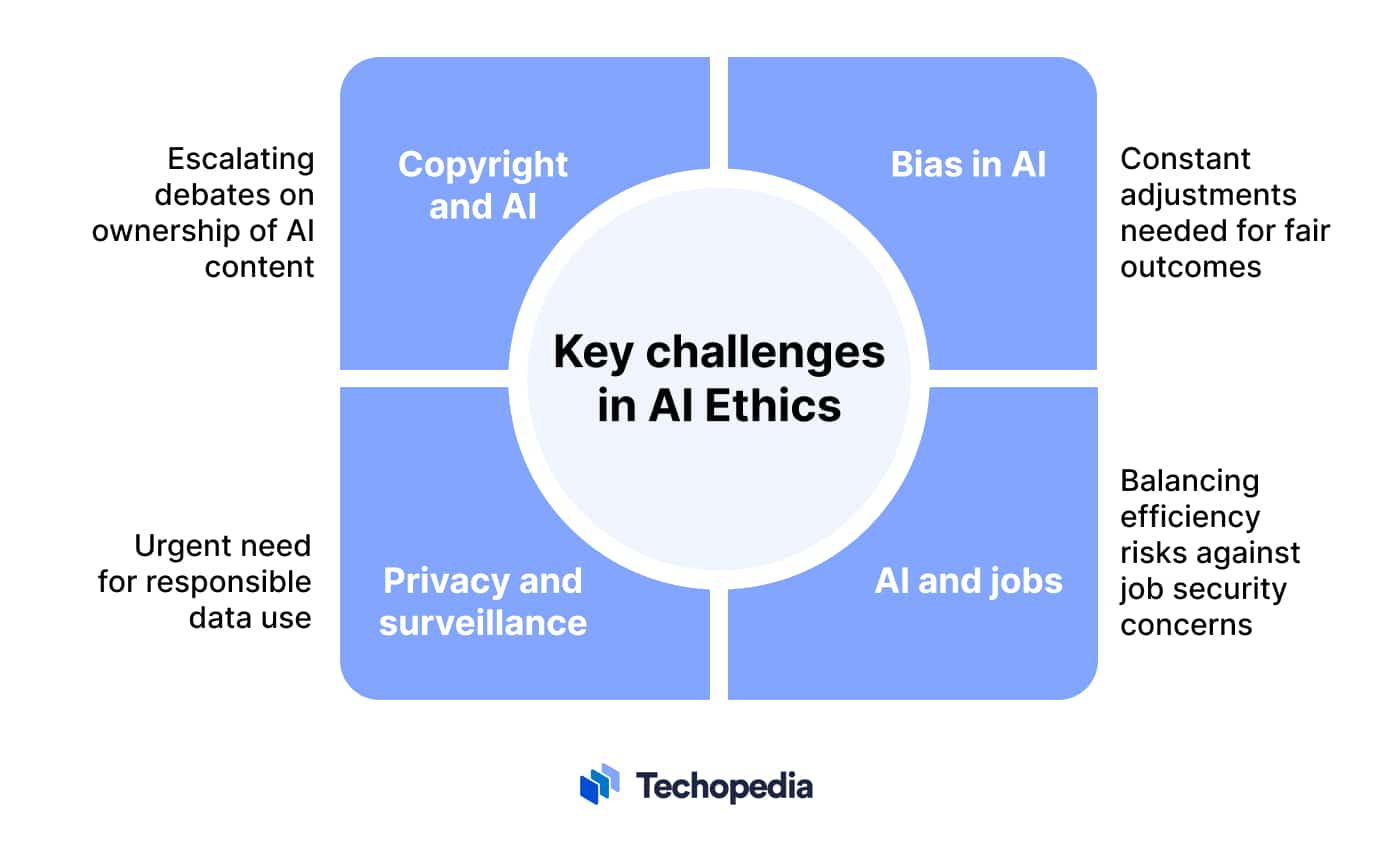
In the field of AI ethics, several key challenges are sparking debates:
- Bias in AI: A big issue with AI is that it can be biased. Sometimes, AI systems make decisions based on unfair or skewed data, leading to unfair outcomes. Fixing this means constantly checking and adjusting AI to ensure it treats everyone equally.
- AI and Jobs: There’s a growing concern about AI replacing human jobs. As AI takes over more tasks, people worry about job security and the future of work. It’s a tough balance between embracing AI’s efficiencies and protecting people’s livelihoods.
- Privacy and Surveillance: AI’s ability to collect and analyze huge amounts of data raises serious privacy concerns. People are worried about how much AI knows about them and what it does with that information. The challenge is to use AI in ways that respect privacy and avoid misuse.
- Copyright and AI: AI can now create its own content, like articles or artwork. This leads to complicated questions about copyright – who owns what AI creates, and how should that content be used? As AI gets more creative, these questions become more pressing.
These challenges highlight the importance of considering ethics in AI development. It’s about making sure AI is not only advanced but also responsible, fair, and respectful of human rights.
AI Ethics Frameworks and Guidelines
As AI technology keeps growing, AI governance is taking over the global and industry stages. Here’s a breakdown of the current AI ethics landscape:
- Global Standards
Big international groups, like the European Union (EU), UNESCO, and the Group of Seven (G7), have set up their own regulations for AI.
- Industry Standards
Big tech companies have their own rules for ethical AI. For example, Google, Microsoft, and Meta have released their own sets of guidelines.
- Academic Contributions
Universities and research centers are also playing a big role in AI ethics. They think about how AI impacts society in the long term and help shape rules that can be practically applied.
- Collaborative Efforts
There are also groups where tech companies, non-profit organizations, and academic experts come together to talk about AI ethics. They work to agree on common ethical standards and best practices. Such groups include Partnership on AI, The IEEE Global Initiative on Ethics of Autonomous and Intelligent Systems, and the AI Ethics Lab.
- Government Regulations
Some countries are beginning to include AI ethics in their laws, making official guidelines for how AI should be developed and used. Countries include the U.K., the U.S., and Canada, among others.
The Bottom Line
AI ethics serves as a guiding principle for the ever-changing world of AI. From its early days in the mid-20th century to today’s comprehensive principles, AI ethics ensures that AI benefits humanity while maintaining fairness, accountability, and respect for individual rights.
As AI continues to evolve, ethics becomes increasingly important. Challenges like bias, job displacement, privacy concerns, and copyright issues highlight the significance of ethical considerations in AI development.
With global standards, industry guidelines, academic contributions, collaborative efforts, and government regulations, the field of AI ethics sets the course for responsible and equitable AI advancements.